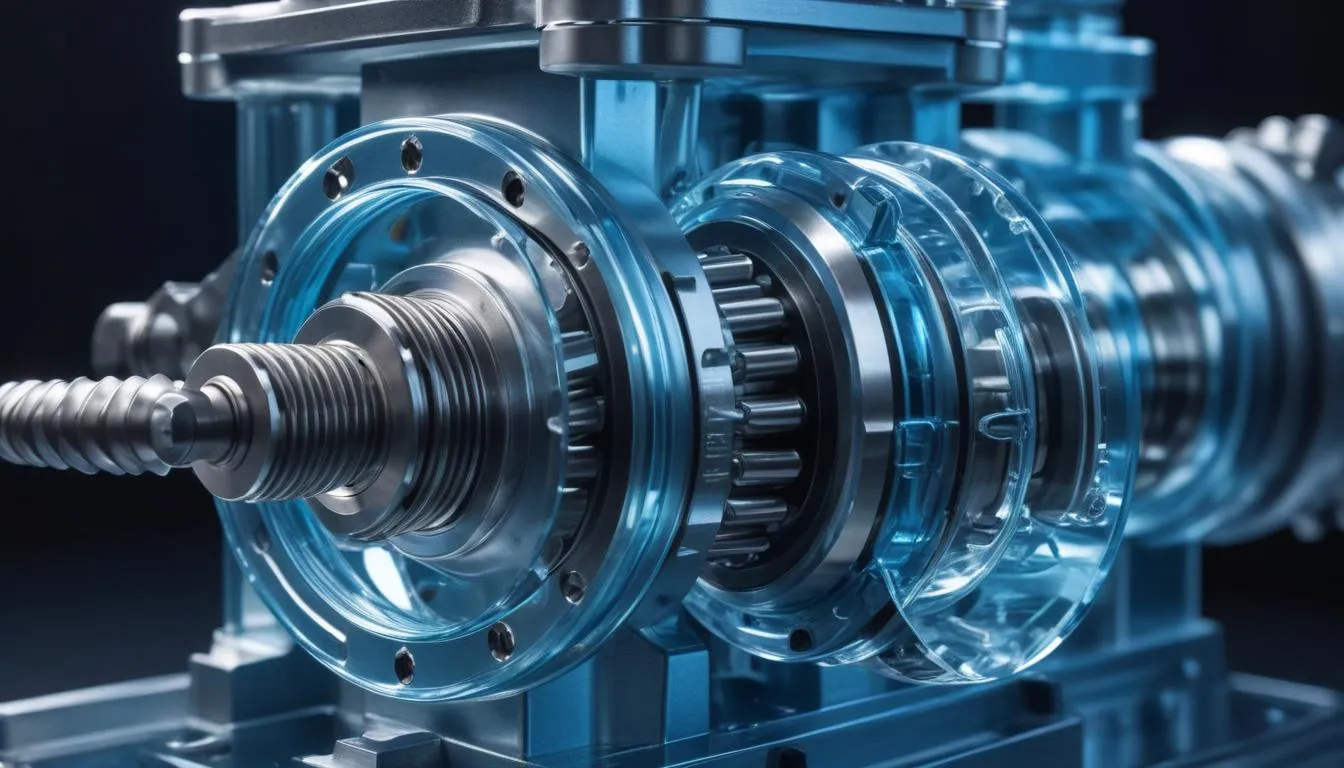
 A screw pump is a type of positive displacement pump that utilizes one or more screws to move fluids. This mechanism involves a rotating screw that moves the liquid along the axis of the screw by transferring energy from the screw to the fluid, which results in the fluid being pushed through the pump. The pump typically consists of a screw rotor and a stationary housing that contains the screw.
A screw pump is a type of positive displacement pump that utilizes one or more screws to move fluids. This mechanism involves a rotating screw that moves the liquid along the axis of the screw by transferring energy from the screw to the fluid, which results in the fluid being pushed through the pump. The pump typically consists of a screw rotor and a stationary housing that contains the screw.
The operation of a screw pump relies on the intermeshing of two or more screws, which can be configured in various ways, including single-screw, twin-screw, and multi-screw designs. As the screws rotate, they create a series of cavities or chambers that expand and contract, allowing the fluid to be drawn into the pump and subsequently discharged at a higher pressure.
The flow characteristics of a screw pump are highly favorable for many applications because of its ability to handle a wide range of viscosities and its capability to deliver a smooth, continuous flow. The design minimizes the turbulence and shear stress applied to the fluid, making it especially suitable for sensitive fluids.
Here are some key aspects of the working principle of a screw pump:
- The rotation of the screw generates pressure through mechanical interaction.
- Fluids are drawn into the pump’s inlet as the screw rotates.
- The fluid is trapped within the cavities formed between the screw and the housing walls, allowing for controlled, steady movement towards the discharge.
- The design creates a low pulsation flow, making it ideal for applications where consistent delivery is critical.
The versatility of the screw pump stems from its ability to accommodate various fluids, including those with high viscosity, and its operational performance remains largely unaffected by changing viscosity levels. Through careful design, screw pumps can also facilitate the handling of abrasive or corrosive fluids, making them valuable in diverse industrial applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The screw pump, while having unique benefits, also presents certain disadvantages that need to be considered when selecting the appropriate pump for specific applications.
Among the main advantages of screw pumps are:
- Smooth Flow Delivery: Screw pumps provide a consistent and steady flow of fluid, minimizing pulsation which is crucial in processes requiring uniform product delivery.
- Handling Viscous Fluids: Screw pumps excel at pumping highly viscous fluids, such as oils or slurries, which may be challenging for other pump types.
- Low Shear Stress: The design of screw pumps reduces turbulence and shear stress, protecting sensitive fluids and reducing the risk of damage to fragile materials.
- Self-Priming Capability: Many screw pumps can self-prime, making them easy to use in applications where priming could be a challenge for other pumps.
- Variable Flow Rates: The speed of the screw rotation can be adjusted, allowing for flexibility in flow rates to meet varying operational needs.
However, there are also disadvantages associated with screw pumps:
- Initial Cost: The complexity of the design and manufacturing process can lead to higher initial costs compared to simpler pump types.
- Maintenance Requirements: Screw pumps may require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance, particularly when handling abrasive or corrosive materials.
- Limited Pressure Capability: While screw pumps can generate considerable pressure, they may not be suitable for applications that require extremely high pressure compared to other pump technologies, like centrifugal pumps.
- Size and Weight: Screw pumps can be bulkier and heavier than other pump types, making installation and mobility more challenging in some settings.
- Noisy Operation: Depending on the design and materials used, some screw pumps can operate with higher noise levels compared to other pumping mechanisms, which could be a consideration in noise-sensitive environments.
It is crucial to evaluate both the advantages and disadvantages when considering screw pumps for specific applications, ensuring that their operational efficiencies align with the requirements of the process while remaining mindful of any potential limitations.
Applications in Various Industries
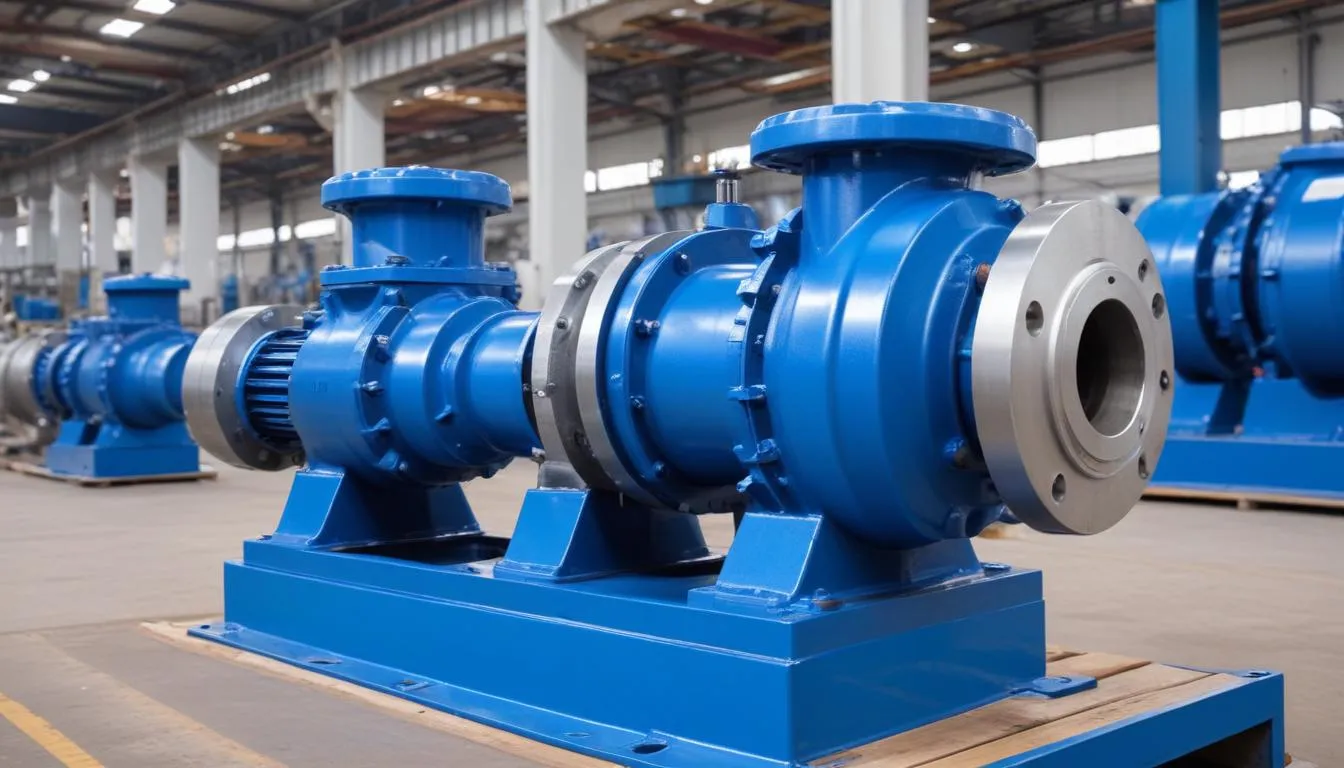 Screw pumps find extensive use across a range of industries due to their unique operating principles and capabilities. Their adaptability to handle various types of fluids, including viscous, abrasive, and corrosive materials, makes them a preferred choice in many applications.
Screw pumps find extensive use across a range of industries due to their unique operating principles and capabilities. Their adaptability to handle various types of fluids, including viscous, abrasive, and corrosive materials, makes them a preferred choice in many applications.
In the oil and gas industry, screw pumps are commonly utilized for the transportation of crude oil and its derivatives. They are effective in moving viscous fluids and can handle varying pressure levels, making them ideal for applications such as well injection, where maintaining consistent flow and pressure is critical. Additionally, their self-priming ability reduces the risk of cavitation, ensuring reliable operation even in challenging conditions.
The chemical processing sector also benefits from screw pumps, particularly for the transfer of chemicals that can be abrasive or corrosive. Their low shear characteristics make them suitable for handling sensitive substances such as polymers and dyes, where maintaining the integrity of the fluid is essential. The ability to customize screw designs allows for optimization based on the specific chemical properties, ensuring efficient and safe transport.
In the food and beverage industry, screw pumps are employed for transferring viscous products like sauces, creams, and pastes. Their gentle pumping action minimizes the risk of damaging delicate ingredients while ensuring a smooth flow. The ease of cleaning and hygiene compliance with sanitary designs further enhance their suitability in this sector.
Pharmaceutical applications utilize screw pumps for the dosing of active ingredients in medications, where precise control and contamination-free environments are paramount. The pumps’ ability to maintain consistent flow rates is crucial for accurate dosing processes, while their capability to handle various viscosities supports the diverse range of formulations found in pharmaceuticals.
For the waste management and wastewater treatment industries, screw pumps are utilized to handle sludge and other thick fluids that require effective transportation to treatment facilities. Their robust design allows for the reliable conveyance of waste materials without clogging, ensuring operational efficiency in challenging environments.
Moreover, screw pumps are also used in the maritime industry for ballast water treatment and bilge pumping applications. The pump’s efficiency in handling water with varying levels of debris or contaminants makes it suitable for keeping vessels in compliance with environmental regulations.
Regardless of the industry, screw pumps are increasingly recognized for their versatility, efficiency, and reliability in fluid handling, underscoring their importance in modern industrial processes.