 Wear rings serve a crucial role in the operation of centrifugal pumps, which are widely used in industries ranging from water treatment facilities to chemical processing plants. These components are designed to maintain hydraulic efficiency, reduce leakage, and protect the pump casing and the impeller from wear due to contact with each other.
Wear rings serve a crucial role in the operation of centrifugal pumps, which are widely used in industries ranging from water treatment facilities to chemical processing plants. These components are designed to maintain hydraulic efficiency, reduce leakage, and protect the pump casing and the impeller from wear due to contact with each other.
The primary function of a wear ring is to provide a replaceable, hard surface that can tolerate the pump’s operational dynamics and maintain a close clearance between the impeller and the pump casing. This close clearance is essential as it minimizes the internal leakage of the fluid being pumped from the high-pressure discharge side of the pump back to the low-pressure suction side. By doing so, wear rings significantly enhance the energy efficiency of the pump and increase its overall performance.
| Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Efficiency Maintenance | Maintains optimal hydraulic conditions within the pump by ensuring minimal clearance and reducing recirculation. |
| Protection | Prevents the impeller and pump casing from coming into direct contact, thereby reducing the rate of wear and extending the lifespan of these major components. |
Additionally, wear rings act as a sacrificial part to protect the impeller and casing from severe damage. This is particularly important in applications handling abrasive or corrosive fluids, where component integrity is crucial to pump functionality. Over time, the wear ring undergoes wear and tear and may require replacement, but this is a more cost-effective solution compared to replacing more expensive components like the impeller or the pump casing.
Material selection for wear rings is paramount and is typically matched with that of the impeller. Common materials include bronze, stainless steel, and various composites, each chosen based on the fluid characteristics and the operating conditions of the pump. For instance, stainless steel wear rings are favored in applications dealing with seawater or corrosive substances due to their resistance to corrosion.
- Bronze: Often used in freshwater applications, known for its decent corrosion resistance and lower cost.
- Stainless Steel: Ideal for seawater and corrosive liquids, offers excellent durability and resistance to corrosion.
- Composites: Suitable for a wide range of applications, generally offering good wear resistance and reduced hydraulic friction.
Equipping centrifugal pumps with wear rings not only improves their longevity and efficiency but also contributes to stable operation and consistent pump performance. Regular inspections and timely maintenance of wear rings are necessary to ensure that the pump runs at its optimal capacity, thus safeguarding against unexpected downtime and repairs.
Installation and maintenance of wear rings
Proper installation and maintenance of wear rings are essential to ensure the efficient and extended operation of centrifugal pumps. The process involves precise handling and alignment to prevent immediate wear or operational inefficiencies.
Installation:
During the installation of a wear ring, it is crucial to adhere to manufacturer specifications to ensure optimal performance. Here is a general guideline:
- Cleanliness: Begin with a clean environment. Ensuring that the area, tools, and components are free of debris will prevent contamination and potential damage during installation.
- Inspection: Thoroughly inspect the new wear ring and the spaces it will be mounted to. Look for any defects or irregularities that could affect performance.
- Alignment: Proper alignment between the wear ring and the pump impeller is critical. Misalignment can lead to rapid wear and efficiency loss.
- Sealing: Make sure that the sealing surfaces are correctly aligned and secured to prevent leakage that could undermine the pump’s performance.
- Testing: After installation, perform a test run to ensure everything operates as intended. Listen for any unusual noises and monitor for abnormal vibrations that could indicate installation issues.
Maintenance:
Routine maintenance of wear rings is as pivotal as proper installation. Maintenance practices include:
- Regular Monitoring: Frequently check the clearance between the wear ring and the impeller. Excessive clearance can reduce pump efficiency and increase operational costs.
- Wear Assessment: Periodically inspect wear rings for signs of degradation or wear. Early detection of wear can prevent more extensive damage to the pump.
- Replacement: Replace wear rings according to the manufacturer’s recommended schedules or more frequently in harsh operating conditions. Always use replacements that match the original specifications for material and dimensions.
Additionally, adhere to the specific guidelines provided by the pump manufacturer regarding the lubrication and cleaning of wear rings, as improper handling can lead to premature failure.
By following these comprehensive steps for the installation and ongoing maintenance of wear rings, operators can significantly enhance the lifespan and efficiency of their centrifugal pumps, ensuring a reduction in both downtime and long-term operational costs. Regular, structured maintenance not only helps in maintaining the pump’s performance but also safeguards other critical components from undue stress and wear, thereby promoting overall reliability and safety in industrial settings.
Common wear ring issues and solutions
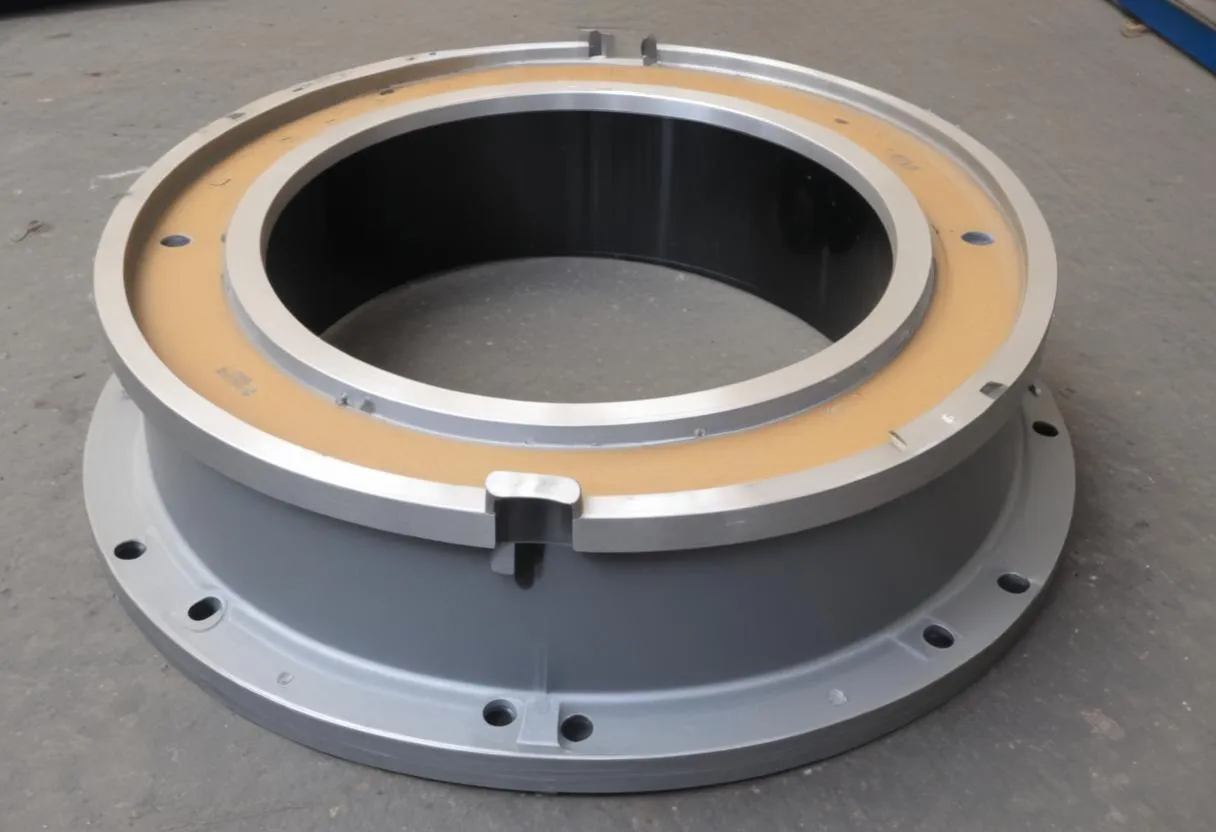 Common issues with wear rings in centrifugal pumps can significantly impact the system’s performance and longevity. Understanding these problems and their respective solutions is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and preventing costly repairs or replacements.
Common issues with wear rings in centrifugal pumps can significantly impact the system’s performance and longevity. Understanding these problems and their respective solutions is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and preventing costly repairs or replacements.
Erosion and Corrosion:
One major problem encountered with wear rings is erosion, particularly in pumps handling abrasive fluids. Corrosion can also occur when the wear rings are exposed to aggressive chemicals.
Solutions:
- Materials: Selecting wear rings made from materials suitable for specific applications, such as alloy composites or hardened stainless steel, can combat erosion and corrosion.
- Coatings: Applying protective coatings can extend the life of a wear ring by providing an additional layer of resistance against harsh elements.
Excessive Wear:
Excessive wear occurs due to improper clearance settings or the presence of abrasive particles in the fluid, leading to increased clearance over time that diminishes pump efficiency.
Solutions:
- Regular Inspections: Monitor and measure the clearance regularly to ensure it remains within specifications.
- Corrective Maintenance: Adjust or replace the wear ring when wear exceeds the acceptable limit.
Galling:
Galling is a form of wear caused by adhesion between sliding surfaces, often seen in pumps with similar metal wear rings and impellers.
Solutions:
- Material Diversity: Using wear rings made from materials different from the impeller can reduce the risk of galling.
- Lubrication: Although not always applicable, in certain environments, enhanced lubrication at the wear surfaces can help mitigate galling.
Deformation:
Thermal deformation can happen when the pump operates at high temperatures, compromising the wear ring’s integrity and pump efficiency.
Solutions:
- High-Temperature Materials: Employ wear rings fabricated from materials that can withstand the operating temperatures without deforming.
- Thermal Analysis: Perform a thermal analysis during the design phase to predict and mitigate potential issues related to heat.
Installation Errors:
Improper installation can lead to premature wear, vibration, and inefficiency in the pump operation.
Solutions:
- Training: Ensure that technicians are properly trained in the installation procedures specific to the pump and wear rings.
- Following Manufacturer Guidelines: Adhere strictly to the manufacturer’s specifications for installation.
- Verification: Always perform a thorough check and testing after installation to confirm everything is set up correctly.
By addressing these common issues with targeted solutions, operators can significantly extend the service life of both the wear rings and the entire pump system. Preventative maintenance and strategic upgrades play key roles in minimizing downtime and promoting continuous, efficient operation of centrifugal pumps.