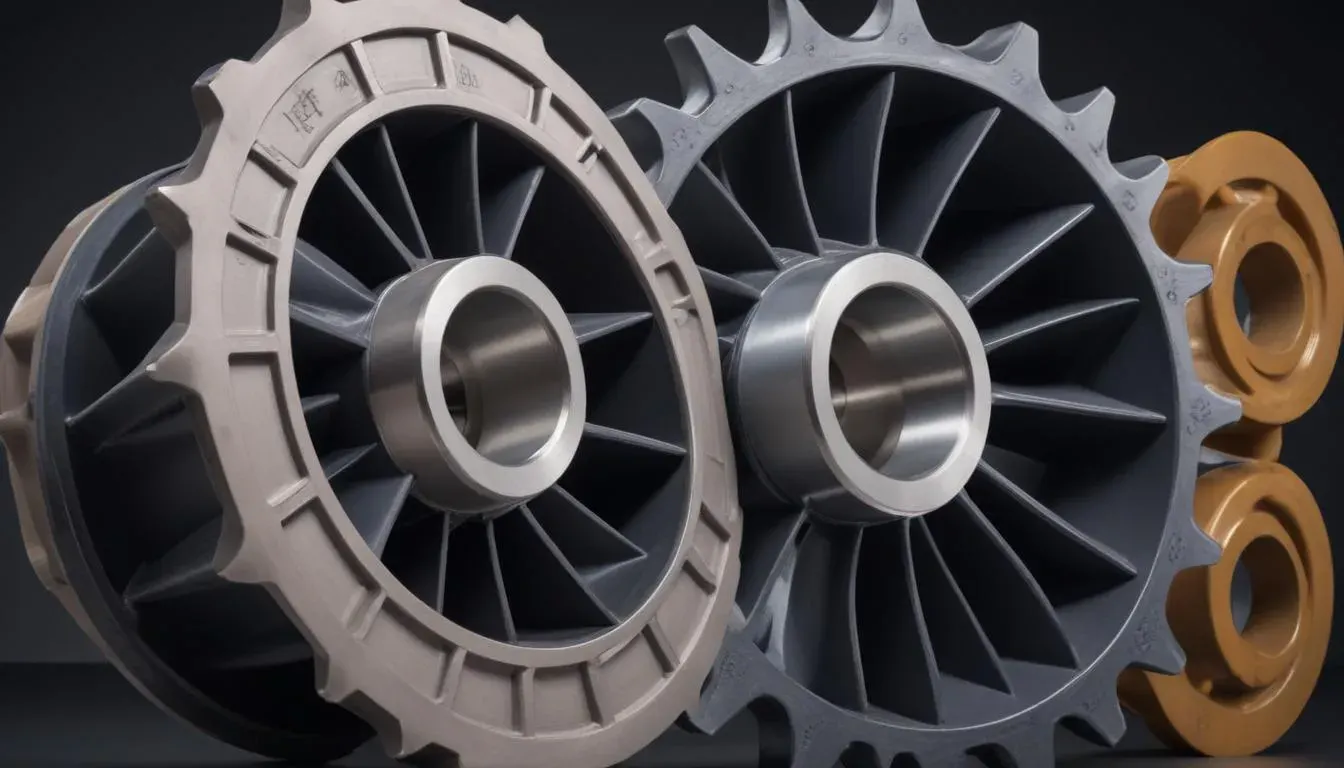
 Pumps are essential devices used across various industries for transporting fluids. The components of a pump play a critical role in its efficiency, durability, and operational effectiveness. Understanding the core components involves looking closely at the materials used, specifically the differences between rubber components and metal components.
Pumps are essential devices used across various industries for transporting fluids. The components of a pump play a critical role in its efficiency, durability, and operational effectiveness. Understanding the core components involves looking closely at the materials used, specifically the differences between rubber components and metal components.
Each component’s material directly affects the performance and lifespan of the pump. For example, rubber components typically exhibit excellent flexibility and resilience, making them suitable for handling a wide range of fluids, including those with varying temperatures and corrosive properties. In contrast, metal components provide a greater degree of strength and durability, which is essential for high-pressure applications and in environments where mechanical wear is prevalent.
The main components of a pump usually include:
- Impellers: The core components responsible for moving the fluid.
- Seals: Critical for preventing leaks and maintaining pressure.
- Casing: Encloses the essential parts of the pump.
- Bearings: Support the rotating shaft and reduce friction.
- Connecting rods: Assist in transferring motion from the motor to the impeller.
When comparing rubber and metal materials, several factors come into play. For instance, rubber components are generally less expensive and easier to replace, while metal components offer longer-lasting performance in challenging environments. It is important to analyze these aspects based on the specific requirements of the application at hand, as each material has its unique properties that influence the pump’s functionality and maintenance needs.
Choosing between rubber and metal components will greatly depend on the operational environment, the type of fluids being handled, and the desired longevity of the pump system. Understanding these components is crucial for ensuring pump reliability and efficiency.
Rubber Pump Components
 Rubber pump components are widely used due to their unique properties that cater to a variety of fluid handling applications. These components, known for their elasticity and resistance to deformation, offer numerous advantages, particularly in settings where flexibility and chemical resistance are paramount.
Rubber pump components are widely used due to their unique properties that cater to a variety of fluid handling applications. These components, known for their elasticity and resistance to deformation, offer numerous advantages, particularly in settings where flexibility and chemical resistance are paramount.
Impellers made from rubber are decidedly lighter than their metal counterparts, resulting in reduced energy consumption during operation. The flexibility of rubber allows for smooth fluid flow, minimizing turbulence and enhancing pump efficiency. As a result, rubber impellers are often employed in applications where cavitation, or the formation of vapor bubbles, may occur.
In terms of seals, rubber provides an effective barrier against leaks, particularly in low-pressure conditions. High-quality rubber seals can accommodate slight misalignments and thermal expansion, reducing wear on the pump components. Certain types of rubber, such as nitrile or fluorocarbon, are specifically engineered to handle harsh chemicals, making them ideal for applications involving aggressive fluids.
The casing of pumps can also incorporate rubber components, offering impact resistance and reducing the risk of damage in environments where external impacts may occur. The inherent properties of rubber provide a cushioning effect, absorbing shocks during operation.
Maintenance and replacement of rubber components tend to be simpler and more cost-effective when compared to metal components. The materials used for rubber parts are often readily available, allowing for quick repairs and minimizing downtime. Bearings designed with rubber can also dampen vibrations, contributing to a quieter operation overall.
However, it is essential to consider the limitations of rubber components. While they excel in flexibility and resistance to certain chemicals, they may not be suitable for high-temperature or high-pressure applications. Prolonged exposure to extreme conditions can lead to degradation, resulting in a shorter lifespan compared to their metal counterparts.
In comparing various rubber components, it is crucial to evaluate their specific formulations and properties, as not all rubber is created equal. For instance, natural rubber provides excellent resilience and stretch, while synthetic options focus on durability and resistance to chemicals.
To summarize, rubber pump components offer distinct advantages in many applications, particularly those that benefit from elasticity, impact resistance, and easy maintenance. Assessing the specific needs of an application will help determine whether rubber components are the most suitable choice, especially when considering cost and repair capabilities alongside performance.
Metal Pump Components
 Metal pump components are integral to the reliability and performance of pumps across a spectrum of applications. Metal components are characterized by their strength, durability, and resistance to wear, making them particularly advantageous in environments subject to high pressure, mechanical stress, and abrasion. The selection of metal components is often driven by the specific demands of the application, including factors such as fluid characteristics, operational conditions, and the expected lifespan of the pump.
Metal pump components are integral to the reliability and performance of pumps across a spectrum of applications. Metal components are characterized by their strength, durability, and resistance to wear, making them particularly advantageous in environments subject to high pressure, mechanical stress, and abrasion. The selection of metal components is often driven by the specific demands of the application, including factors such as fluid characteristics, operational conditions, and the expected lifespan of the pump.
In the realm of pump design, the most common metal components include:
- Impellers: Generally made from high-strength alloys, these components are designed to handle the forces exerted by high-pressure fluids, enabling efficient fluid movement.
- Seals: Metal seals are often chosen for their ability to maintain integrity in extreme conditions and provide robust sealing capabilities in a range of pressures.
- Casing: The casing, usually manufactured from ductile iron or stainless steel, houses the internal components and protects them from external elements.
- Bearings: Metal bearings are preferred for their capacity to withstand high loads and minimize friction, which is crucial for effective operation and longevity.
- Connecting rods: These components typically consist of forged metal, ensuring strong transmission of force between the motor and the pump’s impeller.
One of the primary advantages of using metal pump components is their high-temperature tolerance. Unlike rubber components, which may degrade under extreme thermal conditions, metal can operate effectively in a broader temperature range, making it suitable for various industrial applications, including chemical processing and oil refineries. Furthermore, metal components are inherently resistant to abrasion and can sustain operation without significant wear over an extended period, particularly when handling slurries or particulate-laden fluids.
Another critical factor to consider is the maintenance and serviceability of metal components. Although they offer longer lifespans, any wear or damage that does occur can be more challenging to repair than rubber components. However, advancements in welding and machining technologies have improved the ability to refurbish and extend the life of metal parts economically.
When assessing the comparison between rubber and metal pump components, one key aspect is the operational environment. Metal components excel in contexts where corrosion resistance is vital, such as when handling aggressive chemicals or solvents. Choices in metals, such as stainless steel or specially coated alloys, can enhance resistance to such chemicals.
However, the initial cost of metal components is often higher than that of rubber alternatives, making it essential for operators to evaluate the long-term implications of component choice. While rubber parts might require frequent replacements, leading to higher cumulative costs, metal components, although more expensive upfront, can result in savings over time due to their longevity and reduced maintenance needs.
In summary, various factors underline the selection of metal components in pump applications, including strength, durability, temperature and corrosion resistance, along with long-term cost efficiency. Understanding these properties and how they relate to specific operating conditions can significantly impact the effectiveness and reliability of pump systems in various industries.
Comparative Advantages and Disadvantages
 When evaluating the advantages and disadvantages of rubber and metal pump components, it’s essential to consider multiple factors that affect their performance and suitability for specific applications. Each material exhibits characteristics that can significantly influence the pump’s efficiency, maintenance, and overall cost-effectiveness.
When evaluating the advantages and disadvantages of rubber and metal pump components, it’s essential to consider multiple factors that affect their performance and suitability for specific applications. Each material exhibits characteristics that can significantly influence the pump’s efficiency, maintenance, and overall cost-effectiveness.
Advantages of Rubber Components
1. Flexibility and Resilience: Rubber pump components are highly flexible and can accommodate various fluid dynamics, making them ideal for applications that require adaptability.
2. Cost-Effectiveness: The initial cost of rubber components tends to be lower than that of metal components. This affordability is particularly beneficial in industries where frequent part replacement is necessary.
3. Ease of Installation and Maintenance: Rubber components typically require less intensive maintenance and are easier to install and replace compared to metal parts, reducing system downtime and service expenses.
4. Chemical Resistance: Certain rubber formulations, such as fluorocarbon and nitrile, provide excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals and corrosive substances, enhancing their applicability in chemical processing.
5. Noise Reduction: Rubber components can dampen vibrations and reduce operational noise, contributing to a quieter working environment.
Disadvantages of Rubber Components
1. Temperature and Pressure Limitations: Rubber is not suitable for high-temperature or high-pressure applications. Prolonged exposure to extreme conditions can lead to deterioration and loss of resilience.
2. Wear and Tear: Rubber components may not handle abrasive materials well over time, resulting in a shorter lifespan in specific environments compared to metal options.
3. Limited Strength: While rubber components are flexible, they lack the strength and durability that metal components offer, making them less ideal for high-stress applications.
Advantages of Metal Components
1. Strength and Durability: Metal pump components provide exceptional strength and are resistant to abrasion, making them suitable for high-stress environments, including those involving heavy-duty operations.
2. High-Temperature Performance: Metal components can operate in extreme temperatures, extending their applicability in industries such as oil refining or chemical manufacturing.
3. Corrosion Resistance: Specific metals, like stainless steel, are engineered to withstand corrosive environments, ensuring longevity and reliable functionality.
4. Robust Sealing Capacity: Metal seals are designed to maintain integrity under various pressures and conditions, enabling effective containment of fluids.
Disadvantages of Metal Components
1. Higher Initial Costs: The upfront investment for metal components is generally higher than for rubber components, which can be a deciding factor for budget-sensitive projects.
2. Complex Repair Processes: While metal components have a longer lifespan, repairing damaged metal parts can be more complicated and costly compared to rubber, especially when welding or machining is required.
3. Weight: Metal components are heavier than rubber counterparts, which can impact the overall weight and energy efficiency of the pump system.
Comparison Overview
| Feature | Rubber Components | Metal Components |
|—————————-|————————-|————————|
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
| Flexibility | High | Low |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Temperature Resistance | Limited | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (varies by type) | Very good (specific metals) |
| Maintenance | Easy to replace | Often more complex |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
In conclusion, making a choice between rubber and metal components involves careful consideration of the application requirements, including fluid type, operating environment, and cost. Each material offers distinct advantages and disadvantages that should align with the operational goals and expectations of the pump system in use. Understanding this comparison will empower decision-makers to select the most appropriate components to enhance their pump’s performance and reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
 Choosing the right materials for pump components is critical to achieving optimal performance and reliability in any application. When deciding between rubber components and metal components, several key aspects must be taken into account to ensure the selected materials align with the specific operational demands and environmental conditions.
Choosing the right materials for pump components is critical to achieving optimal performance and reliability in any application. When deciding between rubber components and metal components, several key aspects must be taken into account to ensure the selected materials align with the specific operational demands and environmental conditions.
Firstly, consider the nature of the fluids being handled. If the fluids are corrosive or require a gentler handling approach, rubber components may be ideal due to their flexibility and chemical resistance. On the other hand, if the application involves abrasive materials or operates under high mechanical stress, then metal components should be prioritized for their durability and strength.
Another crucial factor to assess is the working environment. High-temperature conditions often necessitate the use of metal components, as rubber may degrade and lose functionality under such extremes. For environments where chemical exposure is a concern, evaluating the specific formulation of rubber can provide insight into its suitability. Certain rubber types, such as fluorocarbon, offer impressive resistance to harsh chemicals, making them a viable option in chemical processing.
Operational costs also play a significant role in the decision-making process. While rubber components generally come with lower initial costs and easier maintenance, it’s essential to consider the lifetime costs associated with frequent replacements. Conversely, metal components, although more expensive upfront, may lead to considerable savings in the long run due to their longevity and reduced maintenance needs.
To further guide the decision-making process, it can be helpful to compile a list of criteria that are specific to the application’s requirements. These criteria can include:
- Operating temperature range: Determine the maximum and minimum temperatures the pump will encounter.
- Fluid characteristics: Analyze the chemical composition and abrasiveness of the fluids being pumped.
- Pressure demands: Evaluate the pressure levels that the pump components need to withstand.
- Maintenance accessibility: Consider how easy it will be to service the components and perform replacements when necessary.
- Budget constraints: Understand the financial limitations and potential long-term expenses associated with each material choice.
Engaging with engineers and pump specialists can also provide additional insights, helping to ensure that the chosen components not only meet immediate needs but are also aligned with future operational goals.
By carefully evaluating these factors and aligning them with the characteristics of rubber components and metal components, stakeholders can make informed decisions that significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of their pump systems. The comparison between materials is not merely about immediate performance but also about foresight into the long-term effects of the selection choices made today.