 In recent years, advancements in pump technology have significantly focused on improving efficiency and reducing energy consumption. As global energy needs escalate and environmental concerns rise, the push for more efficient machinery has become paramount. Technological innovations in this area not only ensure sustainability but also offer considerable cost savings in long-term operational budgets.
In recent years, advancements in pump technology have significantly focused on improving efficiency and reducing energy consumption. As global energy needs escalate and environmental concerns rise, the push for more efficient machinery has become paramount. Technological innovations in this area not only ensure sustainability but also offer considerable cost savings in long-term operational budgets.
One of the prominent advancements in the efficiency of pumps involves the enhancement of motor design. Modern pumps are increasingly equipped with high-efficiency motors that leverage advanced electromagnetic fields to reduce energy wastage. These improvements include the use of permanent magnet motors and brushless DC motors which are notable for their ability to operate at high efficiency across a variety of load conditions.
Another key development is the implementation of variable speed drives (VSDs). VSDs allow the pump’s speed to adjust in response to varying process demands, thereby conserving energy when full capacity is unnecessary. For example, in water supply systems, VSDs scale the pump’s operation in accordance with fluctuating water demand throughout the day.
- Enhanced Motor Designs
- Variable Speed Drives
- Intelligent Pump Controls
The adoption of intelligent pump controls and sensors has also been pivotal. These controls optimize pump performance by continuously monitoring and adjusting to data on flow rates, pressure, and power consumption. By integrating with centralized control systems, pumps can operate at peak efficiency, reacting real-time to any changes in system demand or operational conditions.
To further illustrate the impact of these innovations, consider the following data points:
| Technology | Energy Savings | Operational Efficiency Increase |
|---|---|---|
| High-efficiency Motors | Up to 10% | 15% |
| Variable Speed Drives | 20-50% | 25-60% |
| Intelligent Pump Controls | 10-30% | 20-35% |
The evidence clearly shows that adopting these innovative technologies can lead to significant reductions in energy use and operational costs, all while promoting sustainability in industry practices. Such advancements are critical as the world moves towards more eco-friendly and cost-effective industrial operations.
Integration of smart technology in pump systems
The use of smart technology in pump systems represents a transformative shift within the industry. These technologies not only enhance the operational functionality of a pump but also contribute greatly to predictive maintenance, system integration, and ultimately, a streamlined management approach.
At the forefront of this transition is the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity. By enabling pumps to connect to the internet, operators can collect critical data in real-time that helps in monitoring system performance and anticipating potential failures before they become critical. This capability effectively shifts maintenance strategies from reactive to proactive, notably enhancing the lifespan and reliability of pump systems.
- Remote Monitoring: Allows for the observation and reporting of pump performance from anywhere in the world, which is indispensable for sprawling industrial complexes or remote locations.
- Automated Control Systems: These systems can adjust operations on-the-fly based on analytics provided by smart sensors integrated within the pump systems.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Employs AI to analyze data and predict failures, facilitating timely maintenance actions that prevent costly downtimes.
Smart sensors incorporated into pumps can detect various parameters such as temperature, pressure, vibration, and flow rates. Here’s how these technologies function together within a smart pump system:
| Smart Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| Temperature Sensors | Monitor and adjust the operating temperature to optimal levels, preventing overheating. |
| Pressure Sensors | Ensure that the system operates within safe pressure limits to avoid mechanical stress and potential system failure. |
| Vibration Sensors | Detect anomalies in operation that may indicate a malfunction or impending breakdown. |
| Flow Sensors | Adjust flow rates to match system demand, enhancing efficiency and reducing waste. |
In addition, the capability for cloud-based analytics furthers the scope of operational enhancements. Data collected from pumps operating in various conditions worldwide can be aggregated in the cloud. This big data is then analyzed to uncover trends and insights, which can be used to optimize performance across all similar pump installations. For instance, if a particular issue is consistently observed in certain conditions, manufacturers can initiate product improvements or develop targeted maintenance strategies that benefit end-users globally.
Ultimately, the integration of smart technology into pump systems fosters not only enhanced operational efficiency and reduced downtime through predictive maintenance and remote monitoring but also enables significant advancements in data utilization and system management. These capabilities are indispensable as industries move towards automation and digitization, pushing the boundaries of traditional pump operation and maintenance into a new era of technological excellence and reliability.
Emerging markets and new applications for pump technology
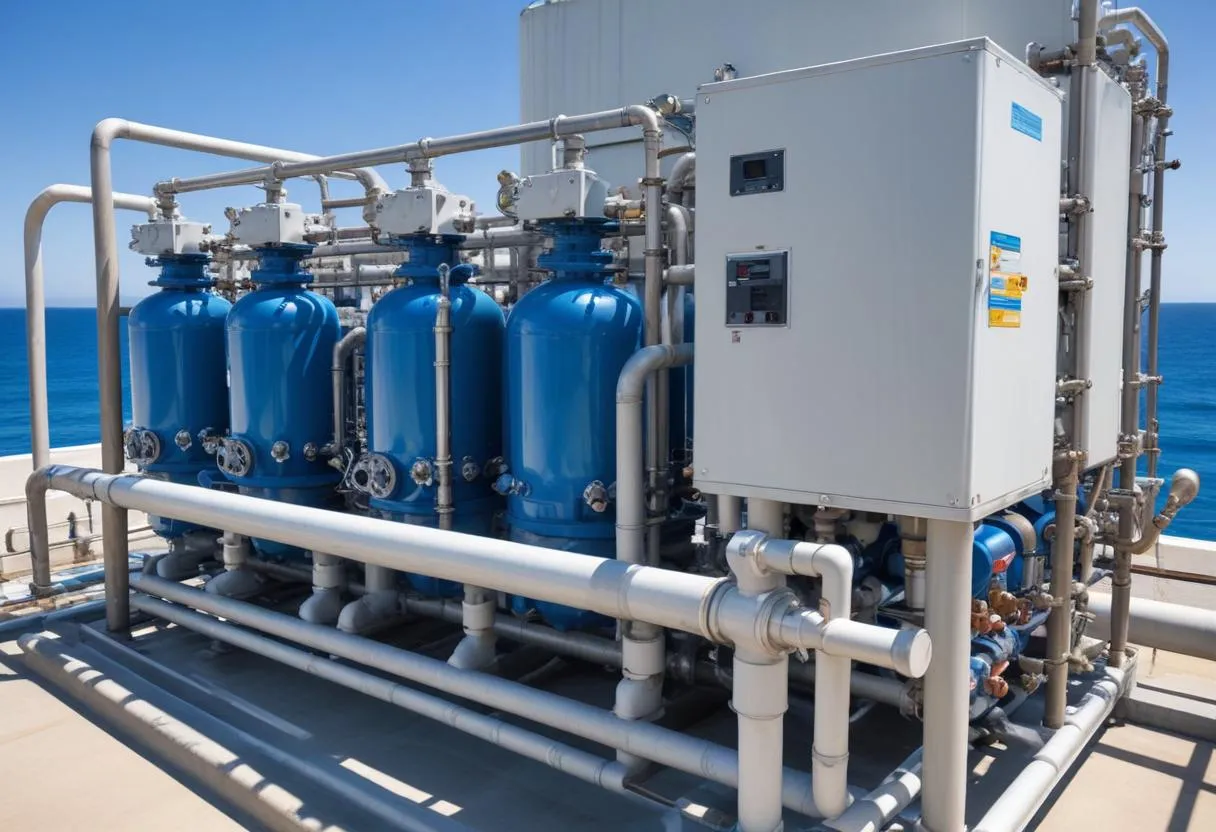 Emerging markets and the innovative applications for pump technology present exciting opportunities across various industries. With urbanization and industrialization accelerating, particularly in developing countries, the demand for advanced pump solutions has surged to support new infrastructures and industries. Here, we explore several promising sectors and how they are leveraging pump technology.
Emerging markets and the innovative applications for pump technology present exciting opportunities across various industries. With urbanization and industrialization accelerating, particularly in developing countries, the demand for advanced pump solutions has surged to support new infrastructures and industries. Here, we explore several promising sectors and how they are leveraging pump technology.
Water Management and Treatment: In regions experiencing rapid urban growth, managing water supply and sanitation efficiently is crucial. Advanced pumping systems are key in facilitating large-scale water transport and treatment projects. Such systems not only ensure reliable water supply but also support wastewater management and flood control initiatives, crucial for maintaining public health and environmental safety.
Desalination Projects: As freshwater resources become scarcer, desalination stands out as a vital technology, especially for water-stressed countries. Pump technology in desalination plants must handle highly corrosive saltwater while minimizing energy consumption to make the process economically viable. The use of high-pressure pumps in reverse osmosis systems is a critical area of innovation, helping to convert seawater to freshwater more efficiently.
Agricultural Advancements: In the agricultural sector, efficient irrigation technologies are pivotal. Here, solar-powered pumps are gaining traction. They offer a sustainable solution by harnessing solar energy to power irrigation systems, reducing dependence on traditional electricity grids and fossil fuels.
Oil and Gas Industries: The extraction and processing of oil and gas are immensely dependent on robust pumping systems. These industries require pumps capable of handling volatile substances under high pressure and temperature conditions. Innovations such as multiphase pumps, which can transport mixtures of oil, gas, and water right from the wellhead, significantly optimize the extraction process.
Mining Operations: In mining, pumps are instrumental for dewatering purposes—removing water accumulated in mines to ensure safety and operational efficiency. Companies are investing in intelligent pump systems that automatically adjust to varying water levels, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Let’s couple these emerging applications with technical potential. Consider adopting pump technology in these key sectors:
- Urban Development: Supporting city infrastructure through improved water circulation and waste management systems.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Implementing solar-powered and precision irrigation systems to boost crop yield with minimal environmental footprint.
- Energy Sector: Enhancing oil, gas, and renewable energy production through efficient and safe pump technologies.
The potential for integrating pumps in these sectors showcases a symbiosis between technological advancement and market needs, paving the way for both economic and environmental benefits. As emerging markets continue to develop, the role of advanced pump technology will likely expand, spearheading innovations across different industrial landscapes. This trend not only highlights the versatility of pump technologies but also their critical role in sustainable development globally.